서 론
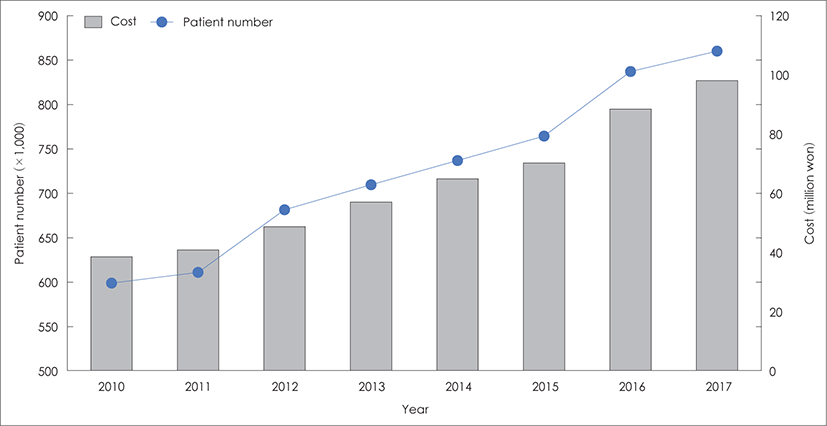
국내의 어지럼 환자는 꾸준히 증가하는 추세를 보이 고 있다. 국내 국민건강영양조사(2010~2012) 결과로는 성인의 21.7%가 최근 1년사이에 주관적인 어지러움을 경험하였으며, 나이가 증가할수록 주관적 어지러움을 호소하는 비율은 높아졌다.1) 건강보험심사평가원 빅데 이터(https://opendata.hira.or.kr)에 따르면, 어지럼 진 단코드인 R42.0으로 진료받은 환자는 2010년 59만명에 서 2017년 85만명으로 연평균 6% 증가하였으며, 요양 급여비용도 2010년 연간 약 380억 원에서 2017년 약 980억원으로 연평균 17%가 증가하였다(Fig. 1). 이러한 증가추세는 고령화로 더욱 가속될 것으로 보이며 그로 인한 개인의 의료 비용 증가뿐만 아니라 삶의 질 저하로 인한 사회, 경제학적인 손실도 상당할 것으로 판단된다.
어지럼의 치료는 원인질환을 찾아서 내과적 외과적 으로 치료하는 방법이 있으며, 질환에 의해 발생한 전 정기능 이상을 호전시킬 수 있도록 훈련하는 전정재활 치료가 있다.2) 전정재활치료는 Cawthorne-Cooksey 운동으로 대표되는 정해진 양식의 운동을 일률적으로 시행하는 기성운동과, 각 환자의 증상과 장애에 맞게 개별화된 운동을 통하여 어지럼 및 균형장애를 개선시 키는 맞춤 운동으로 나눌 수 있다. 최근의 Cochrane 리 뷰에서는, 일측성 전정기능 저하에 있어서 전정재활은 안전하고 효과적인 치료방법이라고 하였으며,3) 고령환 자 어지러움의 치료에 전정재활을 적용한 경우에도 효 과적으로 치료가 되었다고 하였다.4) 2017년 3월에는 국 내에서 “맞춤전정운동”이 신의료기술로 승인, 고시되었 다(신의료기술의 안전성 및 유효성 평가 고시 개정 2017.3.28 고시 제2017-57호). 이렇게 최근 많은 관심이 모아지고 있는 전정재활치료는 다양한 유인물이나 보 조기기나 영상물 등을 이용하여 시행되고 있으며, 특히 4차 산업혁명의 대두와 함께 많은 연구가 진행되고 있 는 가상현실(Virtual Reality, VR) 기술을 활용하여 재 활치료의 효과를 더 높이려는 연구가 진행되고 있다. 본 종설에서는 이러한 VR 기술을 바탕으로 하는 전정 재활치료에 대한 연구가 대한 관심이 높아지고 점점 늘 어남에 따라 그 최신 지견을 살펴보고 향후 발전방향에 대하여 논의하고자 한다.
본 론
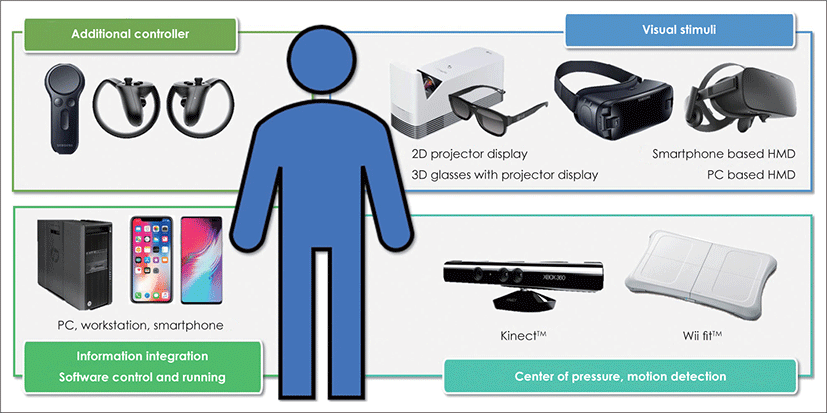
VR 기술은 간혹 다른 범주의 기술과 혼동되어 사용 되곤 한다. 따라서 정확한 개념에 대한 이해가 필요한 데, VR 기술은 현실과 유사한 가상의 허구적 환경이나 상황을 구현하고 이용자로 하여금 마치 실제 환경과 같 이 시각, 청각, 촉각 등으로 감지하고, 상호작용이 가능 하도록 한 기술을 의미하며, 이와 유사하게 자주 언급 되고 있는 증강현실(Augmented Reality, AR)기술은 현 실에 가상의 영상 또는 유의미한 정보를 합성하여 사용 자의 경험이 증강되도록 구현하는 기술을 말한다.5) VR 기술은 다양한 방식으로 구현되는데 2차원 영상을 제시 하거나 가공된 2차원 영상을 바탕으로 3차원으로 인식 될 수 있는 안경을 사용하여 시각적 자극을 제공하고, 센서를 이용하여 동작을 인식하거나 treadmill 위에서 의 움직이면서 시행하는 방법이 이전에는 사용되었다. 하지만 최근에는 체험자가 머리에 장착하여 입체화면 을 표시하고 머리의 움직임을 자이로센서, 가속도 센서 로 감지하여 이를 가상현실에 반영하는 헤드 마운트 디 스플레이(Head mount display, HMD)를 사용하면서 HMD를 제어하고 소프트웨어를 구동하는 PC나 스마 트폰, 추가적인 입력을 가능하게 하는 컨트롤러 등의 사용이 동시에 가능하도록 기술이 발전되었다(Fig. 2). 이러한 VR 기술은 1) 게임, 영상 등 엔터테인먼트 분야, 2) 광고, 쇼핑, 유통 등 서비스업 분야, 3) 교육 컨텐츠, 시뮬레이션 등 교육/미디어 분야, 4) 자동차, 건설, 조선 등 산업분야 5) 의료 분야 등 다양한 영역에 적용되고 발 전하고 있다.6) 특히 의료분야에서는 시장조사업체 MarketsandMarkets의 조사에 따르면 세계 VR/AR 헬스케 어 시장은 2017년 7억 6,920만 달러에서 2023년에는 49 억 9,790만 달러로 연평균 36.6% 성장할 것으로 전망하 고 있어 향후 다양한 영역에서의 적용과 연구가 기대되 고 있다.7)
VR 기술이 처음 의료분야의 접목된 것은 1990년대 참전 이후 외상 후 스트레스 장애를 겪는 환자들의 치 료에 처음 시도되었던 것이었으며, 이후 각종 공포증을 극복하는 치료에 보조적으로 사용면서 점차적으로 적 용 범위가 넓어지고 있다. 최근에는 1) 가상 수술, 해부 학 교육이나 영상진단 보조 등과 같은 의료 교육 분야, 2) 각종 공포증 극복 및 알츠하이머병, 뇌졸중, 전정기 능 저하와 같은 각종 질환에서의 재활, 3) 환자 교육 및 건강관리 목적 등의 영역에서 사용되고 있다.8)
국내에서도 이러한 VR, AR 기술이 적용된 의료기기 에 대한 관심이 증가하고 연구가 점차 진행됨에 따라 관련기기의 허가 심사 가이드라인을 별도로 정하여 연 구의 방향을 제안하고 있다.5) 해당 가이드 라인에서는 VR, AR 기술이 적용된 기기에 대하여 의료기기에 해 당하는 기기와 의료기기에 해당하지 않는 교육 훈련용, 일상적인 건강관리 목적, 사회생활 적응에 도움을 주기 위한 기기로 나누어 허가 심사에 대한 가이드를 제시하 고 있다.
VR 기술이 접목된 의학적 치료의 특징과 장점으로 는 좁고 제한된 공간에서 VR 기반으로 다양한 상황과 프로그램을 체험하여 공간과 비용이 절감된다는 점이 있으며, 환자에게 기존의 경험과는 다른 치료 경험을 제공하여 치료와 재활에 대한 흥미를 높이고 스트레스 해소와 함께 치료에 대한 동기 부여를 높인다는 점, 기 기를 통한 치료과정에서 환자의 움직임이나 순응도 등 을 모니터하여 치료에 대한 관리가 가능하고 치료과정 에 대한 새로운 데이터를 얻을 수 있는 점이 있다.
어지럼을 호소하는 다양한 질환에 대하여 VR 기술을 이용한 전정재활치료가 시도되고 있는데 그 결과 또한 다양하게 보고되고 있다(Table 1).
| Study | Patients/ages | Vestibular problem | Type of virtual reality device | Study setting | Interventions | Treatment method | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Viziano et al. (2019) Clin Rehabil9) | (1) Conventional VR group (n=24) (mean=50.48 years) (2) Mixed (VR+HMD traing)group (n=23) (mean=49.72 years) |
Unilateral vestibular hypofunction | Smartphone with HMD | Randomized controlled trial | Vestibulo-ocular reflex gain Posturographic parameters Fast Fourier transform power spectra, ABC, DHI, DGI |
Head-mounted gaming home exercises, 20 minutes per day for one month 12 month follow up result |
(1) Vestibulo-ocular reflex gain was significantly better with respect to pretreatment in both groups. The mixedmethod group showed significantly higher gain scores (2) Some posturography scores and low-frequency power spectra were significantly different between groups, with the virtual reality group showing improvement (3) Self-report measures were significantly better in both groups compared to pretreatment, with significant improvement in the mixed-method group |
| Rosiak et al. (2019) J Vestib Res10) | (1) Control group (n=25) (mean=45.20 years) (2) Intervention group (n=25) (mean=46.48 years) |
Unilateral peripheral vestibular impairment | Hybrid VR unit (1) Force plate (2) Upper body movement motion sensor (3) Central unit with a flat screen display |
Non-randomized controlled trial | Total length and surface of the COP Vertigo Syndrome Scale–Short Form (VSS-SF) clinical questionnaire |
The exercise protocol consisted of two tasks Ten training sessions lasting 30 minutes for two weeks |
(1) Both the length and square surface of the COP decreased in time (2) Lower score in the VSS-SF questionnaire regarding balance and anxiety subscales (3) Total improvement in patient-reported outcomes compared by group showed statistically significant differences in favor of Virtual reality training |
| Micarelli et al (2017) Int J Rehabil Res.11) | (1) Conventional group (n= 24) (mean=50.48 years) (2) VR with HMD group (n=23) (mean=49.72 years) |
Chronic unilateral vestibular hypofunction | The Track Speed Racing 3D game with HMD | Randomized controlled trial | Vedeo head impulse test Posturography DHI, ABC The Zung Instrument for Anxiety Disorders DGI SSQ |
Perform the 3D game protocol uninterruptedly for 20 min/day for 4 weeks. | (1) Siignificant reduction in surface during eyes closed length during eyes closed and in length during eyes opened conditions in HMD group (2) HMD group showed a significant reduction in power spectra values in eyes closed and eyes opened condition (3) Significant post-treatment VOR gain improvement was found in HMD group (4) Significant post-treatment between-effect changes in DHI and ABC scores in HMD group (5) SSQ reduced significantly after repeated treatment |
| Hsu et al. (2017) Disabil Rehabil.12) | (1) Control group(n= 34) (mean=66.5 years) (2) Study group(n=36) (mean=68.0 years) |
Meniere’s disease | (1) Wii Fit with Wii board (2) Ultrashortfocus projector display and 3D glasses |
Single-blinded randomized controlled trial | (1) Rehabilitation exercise scores (eye, head, extension, cordination) (2) Balance indiced center of gravity sway, SKG maximum mediolateral (maxML) and anteroposterior (maxAP) trajectory excursion mean mediolateral (meanML) and anteroposterior (meanAP) trajectory excursion |
The study group completed the game program in 30 min, and underwent six training session during 4 weeks | (1) In the study group, a significant improvement was observed in all eye, head, extension, coordination, and total training task scores (2) Significant differences were observed in the changes of head rotation and total training task scores between two groups (3) The balance indices exhibited a decreasing trend in the center of gravity sway. The study group exhibited significantly greater improvement in the SKG |
| Meldrum et al. (2015) Arch Phys Med Rehabil13) | (1) Conventional VR group (n= 36) (mean=50.47 years) (2) VR with Wii Fit plus group (n=35) (mean=57.83 years) |
Unilateral peripheral vestibular loss | Wii Fit Plus with Wii Board | Single-blinded randomized controlled trial | (1) Gait parameters : speed, step length, step width, and percentage of gait cycle spent (i) Self-preferred gait speed (m/s) (ii) Walking with head turns (as per the Dynamic Gait Index task) (iii) Walking with eyes closed (distance, 3.75 m) (iv) DGI (2) Standing balance (i) Equitest’s SOT (3) Dynamic visual acuity (4) Subjective measure (i) Vestibular Rehabilitation Benefits Questionnaire (ii) ABC (iii) Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale score total |
Gaze stabilization exercises, balance exercises, graded walking program for 6 weeks | (1) No significant differences between the groups in self preferred gait speed at 8 weeks (2) The Equitest SOT scores were no significant differences between groups. (3) DVA data showed no significant difference between groups (4) VR with wii fit group reported significantly more enjoyment, less tiredness and less difficulty with the balance exercises |
| Alahmari et al. (2014) IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng.14) | (1) Customised vestibular rehabilitation group (n= 18) (mean=61 years) (2) Virtual reality based therapy group (n=20) (mean=53 years) |
Peripheral, central, or mixed vestibular disorders | Treadmeal with projector display | Non-randomized controlled trial | (1) Self-report measures ABC, DHI, Situational Characteristics Questionnaire (SCQ) (2) Perfomance measures DGI, SOT, Gait speed, Functional Gait Assessment (FGA) Times Up and GO test (TUG) (3) Within-session symptome measures severity of their nausea, headache, dizziness, and visual blurring using a VAS, SSQ |
Subjects ambulated on a treadmill as if they were moving through aisles in a virtual grocery store. One session per week for 6 weeks | (1) Not a significant effect of group or interaction between group and time for any of the self-report measures and performance measures (2) Significant improvement in self-report measures and performance measures (except TUG) immediately after and 6 months after the intervention on both groups (3) VAS, SSQ score increased significantly after session. (4) SSQ reduced significantly after repeated session |
| Yeh et al. (2014) Technol Health Care.15) | n=49 (mean=63 years) | Chronic imbalance problems caused by vestibular dysfunction | (1) 3D interactive vertual reality based rehabilitation system (projector display and 3D glasses) (2) Wii Fit with Wii board for upright balance test |
Case study | (1) Performance data completion rate, time and the number of continuous ball-catching (2) Balance indices maxML and maxAP trajectory excursion. meanML and meanAP trajectory excursion, SKG |
The training system was composed of 4 game-like training tasks simulating Cawthorne-Cooksey exercises. Six training session during 4 weeks. |
(1) For the performance data, the results of comparison between pre-training test and post-training test showed significant improvement in all training scores except the completion rate in head exercise (2) For the balance indices, the results of comparison showed a significant improvement in SKG and maxML |
| Garcia et al. (2013) Braz J Otorhinolaryngol16) | (1) Control group (n=21) (mean=47.9 years) (2) Case group (n=23) (mean=47.65 years) |
Meniere’s disease | Virtual reality goggles, accelerometer and foam cushions | Randomized controlled trial | DHI dizziness VAS center of pressure and oscillation rates in balance rehabilitation Unit | Posturography, body balance rehabilitation, and postural training games. | Virtual reality-based balance rehabilitation effectively improved dizziness, quality of life, and limit of stability of patients with Menière’s disease |
VR : vestibular rehabilitation, HMD : Head mounted display, ABC : Activities-specific Balance Confidence, DHI : Dizziness handicap inventory, DGI : Dy¬namic gait index, COP : Center of pressure, SSQ : Simulator Sickness Questionnaire, SOT : Sensory Organization Test, VAS : Visual analogue score, SKG : Statokinesigram
Viziano 등은 일측성 전정기능 저하 환자 47명을 대 상으로 무작위 배정 연구를 시행하여 고전적 방법의 전 정재활치료를 시행한 군과 고전적 전정재활치료와 함 께 스마트폰과 HMD를 이용한 게임을 한달간 매일 20 분씩 시행한 두 군의 치료 후 결과를 비교하였다. 그 결 과, HMD를 이용한 재활프로그램을 같이 시행한 군에 서 치료 후 1년뒤에 Dizziness handicap inventory(DHI) 와 전정안구반사 이득 등이 기존의 방식보다 유의하게 잘 호전되는 것이 관찰되었다.9)
Rosiak 등은 일측성 말초성 전정기능 환자 50명을 대 상으로 비 무작위 배정 연구를 시행하였는데, 기존의 대조군에 비하여 VR 기술을 활용한 전정재활치료에서 중심을 더 잘 잡게 되고 주관적인 증상도 호전을 보이 는 것으로 나타났다. 이 연구에서는 압력 감지 판과 상 체의 움직임 감지센서, 평면 스크린이 사용되어 2가지의 운동 프로토콜을 사용하여 전정재활을 진행하였다.10)
Micarelli 등은 다양한 원인의 일측성 전정기능 저하 환자 47명을 대상으로 무작위 연구를 시행하였다. HMD 를 이용하여 머리의 움직임으로 레이싱을 하는 게임 기 반의 전정재활치료를 시행하였다(Fig. 3). 기존의 전정재 활을 시행한 군보다 HMD를 착용하고 하루 20분씩 게임 기반의 전정재활 프로그램을 시행한 군에서 주관적인 DHI와 Activities-specific Balance Confidence가 더 많이 호전되는 것으로 나타났으며, 객관적인 평형관련 수치들 도 호전이 있는 것으로 보고하였다. 또한 이 연구에서는 HMD를 사용한 VR 기반 프로그램을 실행하면서 세션이 반복될수록 Simulator Sickness Questionnaire(SSQ)의 점 수가 호전되는 결과를 보여 훈련을 반복할수록 simulator sickness 가 감소한다는 기존의 연구와 동일한 결과 를 보고하였다.11)

Hsu 등은 메니에르병 환자 70명을 대상으로 전정재 활에 대한 무작위 연구를 시행하였는데, 기존의 전정재 활을 시행한 군과 Wii fit(Wii Fit, Nintendo Phuten Co., Ltd., Taipei, Taiwan)기기와 프로젝터와 3D 안경을 이 용하여 안구 운동, 머리운동, 신전운동, 조합운동을 1회 에 30분정도 6주내 4회 시행한 실험군으로 나누어서 연 구가 진행되었다(Fig. 3). 연구 결과 재활운동 전에 비 하여 재활운동수치가 향상되었고, 실험군에서 머리움 직임과 전체 점수가 대조군에 비교하여 유의하게 향상 되는 경향을 보였다. 또한 평형 관련 수치도 치료 이후 호전되는 경향을 보였다.12)
Meldrum 등은 일측성 말초성 전정기능 저하 환자 71명을 대상으로 무작위 배정 연구를 시행하여 고전적 인 방법의 설명문을 제공한 전정재활치료와 Wii Fit plus 와 사용자의 무게 중심을 분석하여 환자의 움직임을 추 정하는 Wii board를 이용한 전정재활치료를 시행한 두 군의 치료 후 결과를 비교하였는데 치료 이후 두 군 모 두 보행속도와 기립시 균형 능력이 호전되었으나 두 실 험군 간의 차이는 없었으며, VR 기술을 이용한 군에서 환자들은 프로그램을 어렵지 않게 느꼈으며, 치료 이후 피로감을 덜 느꼈다.13)
Alahmari 등은 말초성, 중추성, 혼합성 전정기능 이 상 환자를 대상으로 하여 18명은 맞춤형 전정 재활을 시행하고 20명은 treadmill 앞으로 프로젝터를 이용하 여 가상의 상점 통로를 구성하여 통로를 돌아다니고 가 상의 물건을 이동시키는 VR기술을 이용한 전정치료를 시행하였다(Fig. 3). 그 결과 두 군 모두에서 주관적 수 치와 보행속도 등 객관적 수치 모두 호전되는 것이 관 찰되었으나 두 군사이에 유의한 차이는 없었다. VR 기 술을 이용한 전정재활치료를 시행한 군에서는 치료를 시행한 후 오심, 두통, 어지러움 등 증상이 유발되는 것 으로 나타났으나 기존의 연구와 마찬가지로 이러한 증 상과 SSQ는 치료에 대한 노출이 지속될수록 감소하는 양상을 보였다.14)
Yeh 등은 49명의 전정기능 저하로 인한 만성적인 평 형 이상 환자를 대상으로 Cawthorne-Cooksey 운동을 기본으로 한 4가지의 게임으로 구성된 전정재활 치료를 시행하였으며, 치료 전후에 유의미한 기능 호전이 있는 것으로 보고하였다.15)
Garcia 등은 메니에르병 환자 44명을 대상으로 전정 재활에 대한 무작위 연구를 시행하였는데, 기존의 전정 재활을 시행한 군과 VR 기술이 사용된 고글과 무게중 심, 가속도 센서가 사용된 시스템을 이용하여 posturography, 신체 평형 재활, 자세 훈련 게임을 시행하여 전 정재활을 시행하였는데 재활치료 시행이후 VR 기술을 이용한 군에서 Dizziness handicap inventory, VAS 등 의 통계적으로 유의하게 호전된 것을 확인하였고 대조 군과 비교해서도 더 나은 결과를 나타냈다고 하였다.16)
이처럼 다양한 연구들이 진행되고 있지만 VR 기술 을 이용한 전정재활치료에도 아직 극복해야할 문제들 이 있다. 첫번째로, 전정재활 프로그램 자체를 시행하면 서 겪는 simulator sickness로 인하여 어지럼을 추가로 겪을 수 있다는 것이다. Simulator sickness는 멀미와 유사한 위약감, 어지럼, 오심, 두통 등 불쾌한 증상이 가 상 현실 체험을 하는 도중이나 이후에 발생하는 증후군 이다.17) 이러한 증상들은 나이, 성별, 스트레스, 불안의 정도, 체험자의 특성 등에 따라 개인차가 있다. 이러한 증상이 나타나는 원인은 여러 가설이 제시되고 있는데 움직임 자체와 시각, 전정계, 고유감각의 감각계가 서로 상충하면서 이전의 경험과 다르게 인식되어서 유발된 다는 가설과18) 개인이 이전에 경험해보지 못한 상황에 노출되면서 그 상황에서 평형을 어떻게 유지하고 상황 을 보정할 것인지에 대한 경험이 없는 것에서 유발되는 자세 불안정으로 인한 것이다는 가설이19) 일반적으로 받아들여지고 있다. 여러 연구에 따르면 이와 같은 simulator sickness는 VR 환경에 노출이 길어질수록 증상 이 심해지고, VR 환경에서 움직임을 제어하는 방법(조 종간, 실제 보행 등)에 따라 증상의 정도가 달라지며, VR 환경 체험이 종료된 이후에도 증상이 나타날 수 있 다고 한다.17) 따라서 VR 기술을 이용한 전정재활에 대 한 연구에서는 환자의 어지럼 증상에 더하여 simulator sickness에 의한 증상이 병발될 수 있으므로 그에 대한 사전 고지와 치료 과정의 시간에 대한 고려가 있어야 할 것이다. 또한 치료 중 발생할 수 있는 낙상에 대비한 안전장치 설치와 치료 이후에 나타날 수 있는 증상에 대한 대비가 필수적으로 고려되어야 할 것이다.
또 다른 VR 기술을 이용한 전정재활의 한계는 아직 치료 방법의 표준화가 이루어지지 않았다는 부분이다. 전에 기술하였듯이 다양한 연구는 이루어 지고 있으나 사용된 VR 기기, 체험시간, 컨텐츠 제작 방법, 체험 소 프트웨어의 콘텐츠가 다양하고 치료 전후 증상의 호전 을 확인하기 위한 측정 값이 상이하여 이에 대한 가이 드라인과 표준화가 필요한 실정이다. 또한 치료방법의 특징상 무작위 이중맹검법(double-blinded randomized control)에 의한 연구가 어렵고, 현재까지 이중맹 검 무작위배정법을 이용한 연구가 없는 등 과학적이고 양질의 연구가 추가적으로 필요한 상황이다.
결 론
어지럼 환자의 지속적 증가추세는 우리나라의 인구 구조의 변화와 고령화의 가속화, 더 나은 삶에 대한 추 구 등과 같은 원인에 의해 계속될 전망이다. 적절한 문 진과 검사를 통하여 정확한 원인을 찾고 그에 대한 치 료를 시행함으로써 늘어나는 환자에 대한 적절한 대응 이 필수적이지만, 적절한 치료 이후에도 지속되거나 단 순 노화에 의한 비특이적인 어지럼 증상에 대응하기 위 한 전정재활치료의 필요성은 더욱 커지고 있다. 현재까 지 연구되고 있는 일반적인 전정재활 치료에 더하여, 다양한 정보통신기술의 발전을 기반으로 한 VR 기술을 융합한 전정재활치료는 점차 다양하게 시도되고 있다. VR 기술이 접목된 전정재활치료는 다양한 연구에서 주 관적인 증상 호전에 도움이 되고 객관적인 평형지표를 호전시킬 수 있다는 결과를 도출하고 있다. 또한 일부 연구에서는 치료 중 오심, 두통, 어지러움 또는 simulator sickness가 발생할 수 있다고 하였으나 치료를 지속 하면서 계속 노출시키면 그 정도가 감소한다고 보고하 였다. 이러한 효과를 보이는 VR 기술을 이용한 전정재 활치료는 Simulator sickness나 낙상 등 환자 안전 문제 가 필수적으로 고려되어야 할 것이며, 표준화된 치료방 법의 설정, 과학적으로 설계된 연구방법을 통한 연구경 험의 축적 등이 더 이루어져야 할 것이다.






