Case Report
섬유성 이형성증을 모방한 상악동 미만성 거대 B세포 림프종 1예
A Case of Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma on Maxillaly Sinus Mimicking Fibrous Dysplasia
Gyo Han Bae
1
, Ji-Hwan Park
1
, Sung-Dong Kim
1
, Kyu-Sup Cho
1,*
1Department of Otorhinolaryngology and Biomedical Research Institute, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Pusan National University Hospital, Busan, Korea
*Corresponding author: Kyu-Sup Cho, Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Pusan National University Hospital, Busan 49241, Korea, Tel: +82-51-240-7824, Fax: +82-51-246-8668, E-mail:
choks@pusan.ac.kr
© Copyright 2022 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx. This is an Open-Access article distributed under the terms of the
Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) which permits
unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any
medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Received: Dec 01, 2022; Revised: Dec 14, 2022; Accepted: Dec 16, 2022
Published Online: Dec 31, 2022
ABSTRACT
A 38-year-old male came to outpatient clinic, presenting with a 1-month history of headache and right facial pain. There was no specific finding on nasal endoscopy. Paranasal sinuses computed tomography (PNS CT) showed unilateral soft tissue density on right maxillary sinus and ground glass opacity on right maxillary and zygomatic bone. And there was no finding suggestive of malignancy in the subsequent PNS magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). We considered benign tumor such as fibrous dysplasia with maxillary sinusitis and performed the endoscopic sinus surgery combined with open surgery via Caldwell-Luc and subcillary approach. Histopathological diagnosis was diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. After six cycles of rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, prednisolone chemotherapy, he gained complete remission and found no recurrence until two years. We report a rare case of sinonasal lymphoma mimicking fibrous dysplasia with literature review.
Keywords: Lymphoma; large B-cell; diffuse; Maxillary sinus
서론
악성 림프종은 림프 조직에 속하는 세포들인 림프구 및 조직구의 악성종양으로 호지킨 림프종과 비호지킨 림프종으로 크게 나눌 수 있다. 림프절 침범이 많으나, 인체의 어느 부위에서나 발생할 수 있으며, 두경부 영역에서는 Waldeyer’s ring에서 호발한다.1) 비호지킨 림프종(non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma)인 미만성 거대 B세포 림프종(diffuse large B cell lymphoma)은 매우 드물게 동양인의 부비강에 발생한다.2) 저자들은 섬유성 이형성증으로 오인된 상악동 미만성 거대 B세포 림프종을 항암화학요법으로 성공적으로 치험하였기에 문헌 고찰과 함께 보고하고자 한다.
증례
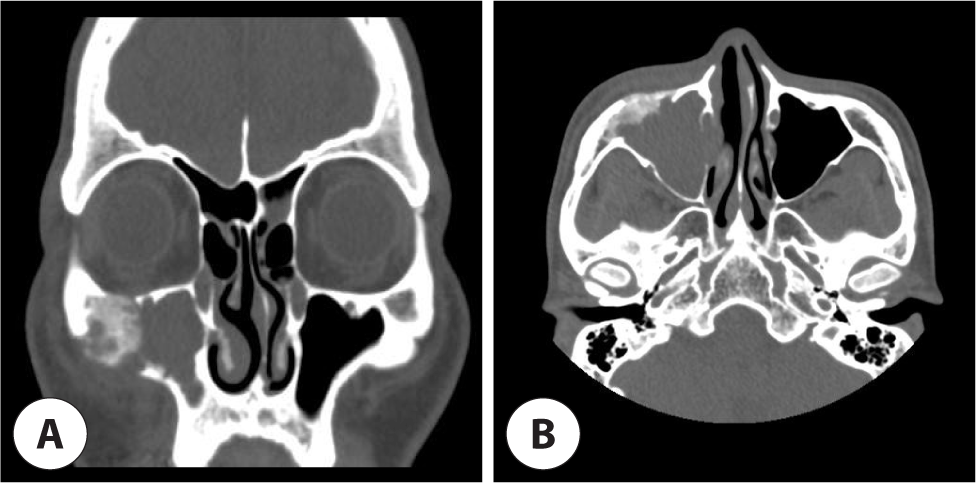
38세 남자가 1개월 전부터 시작된 두통과 우측 안면통을 주소로 타 병원 방문 후 상악동 종양 의증으로 내원하였다. 환자의 과거력, 사회력, 가족력에는 특이 사항이 없었으며, 체중감소, 발열, 야간 발한 등의 전신 소견도 없었다. 신체검진에서 만져지는 두경부 종물은 없었으며 비내시경소견에서 특이 소견은 관찰되지 않았다. 부비동 CT(computed tomography)에서 우측 상악동을 채우고 있는 연조직 음영과 주변 상악골 및 관골에 간유리 음영 (ground glass opacity)이 관찰되었다(Fig. 1). 연조직 음영 감별을 위해 촬영한 MRI(magnetic resonance imaging)에서 상악동 내 연조직은 조영 증강되지 않았으며 T2/T1 강조 영상에서 중간 신호 강도 소견을 보였다(Fig. 2). 이에 악성보다는 섬유성 이형성증과 같은 양성 질환으로 보고, 우측 상악동 내 연조직 병변에 대한 조직검사 및 제거를 위해서 전신마취하 부비동 내시경 수술과 Caldwell-Luc 접근법 및 눈썹하 절개를 통한 외부 접근법으로 수술을 시행하였다.
Fig. 1.
Paranasal computed tomography (CT) scan shows soft tissues density involving the right maxillary sinus with ground glass opacity at right maxillary and zygomatic bone. A : Coronal view. B : Axial view.
Download Original Figure
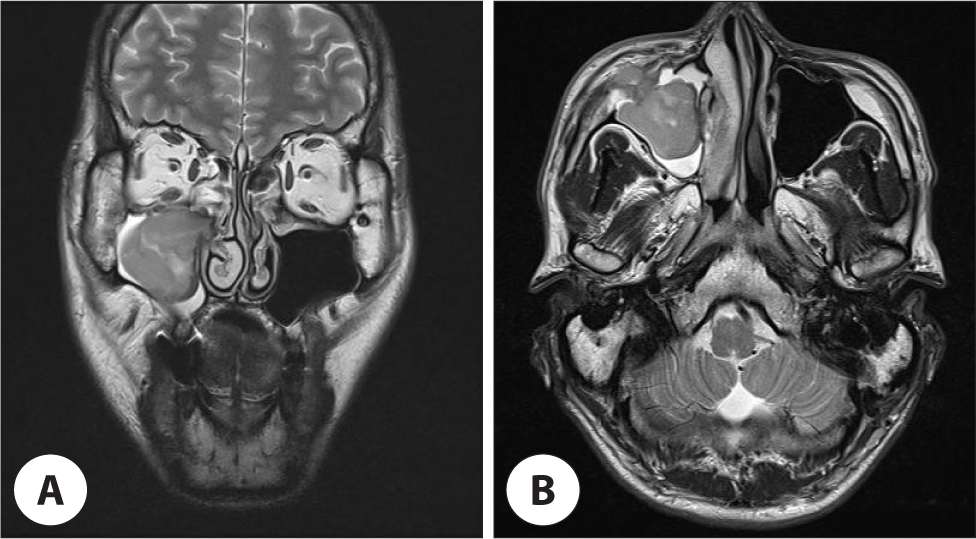
Fig. 2.
Paranasal magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan shows intermediate signal intensity without enhancement on T2 weighted image. A : Coronal view. B : Axial view.
Download Original Figure
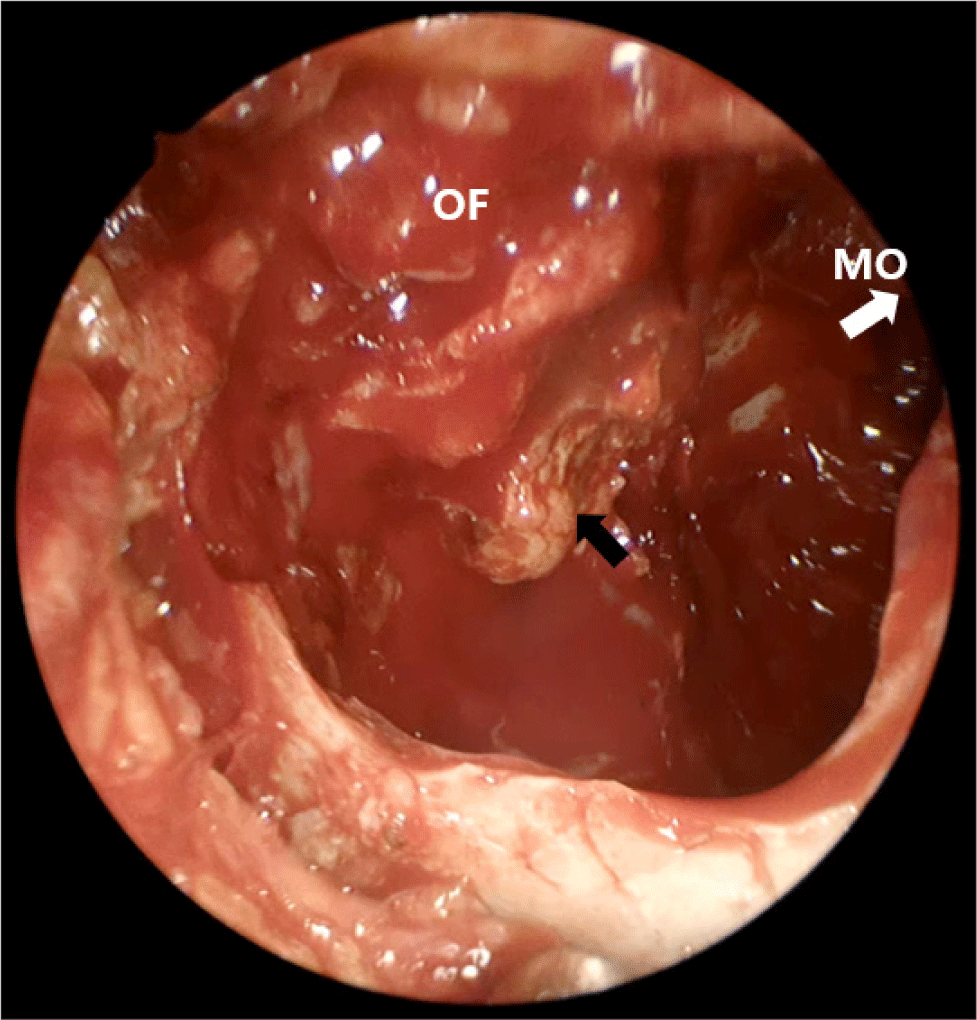
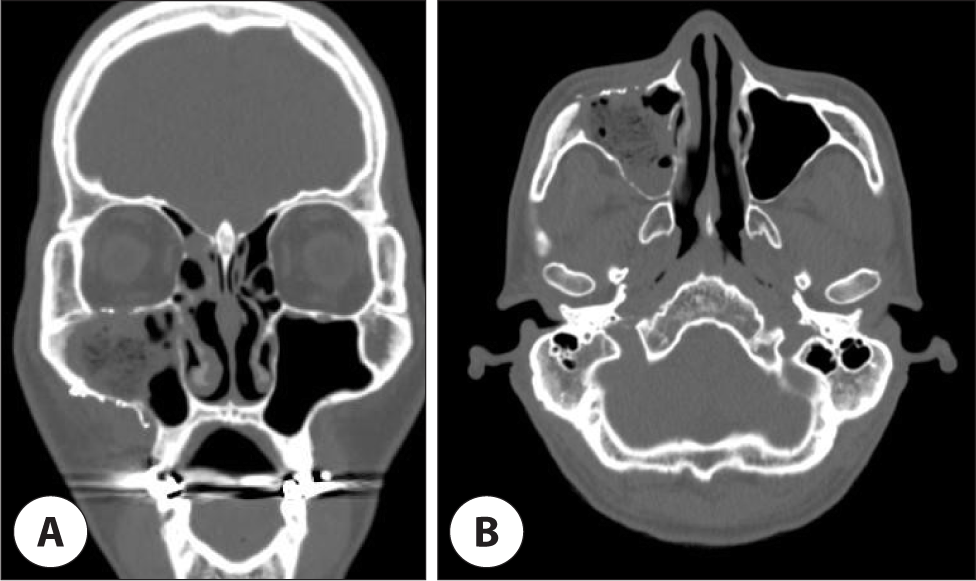
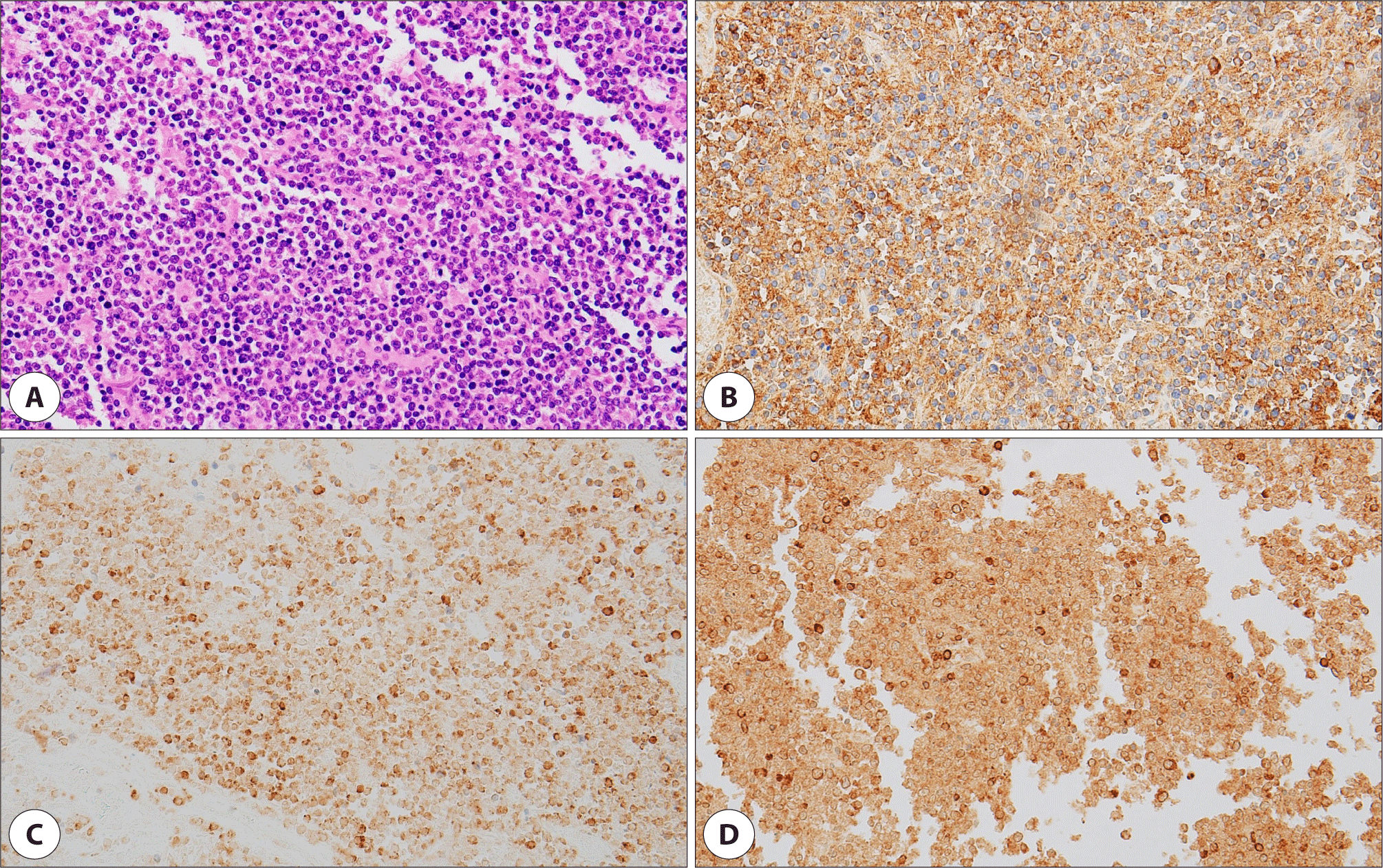
수술 중 국소 소견에서 상악동 점막의 염증성 비후 소견이 있어(Fig. 3) 시행한 동결 절편 검사 결과 만성 염증 및 괴사 소견이 의심되었으며, 이에 섬유성 이형성증으로 생각하고, 섬유성 이형성증은 부분 절제 시 재발 가능성이 있기 때문에 완전 절제를 목표로 우측 부비동 내 종물 제거, 골 미란 병변 제거 및 안와하벽 및 상악동 전벽 결손부에 대하여 재건술을 시행하였다(Fig. 4). 상악동 점막 및 CT 검사상 간유리 음영으로 보였던 상악골 조직의 면역조직화학 검사상 CD20, CD79a, BCL-2에 양성반응을 보여 미만성 거대 B세포 림프종으로 진단되었다(Fig. 5).
Fig. 3.
Intraoperative local finding of right maxillary sinus shows mucosal thickening, Caldwell-Luc approach view (black arrow: biopsy). MO: maxillary ostium, OF: orbital floor.
Download Original Figure
Fig. 4.
Postoperative paranasal computed tomography (CT) scan shows complete removal of soft tissues density involving the right maxillary sinus with ground glass opacity at right maxillary and zygomatic bone and reconstruction with titanium mesh. A : Coronal view. B : Axial view.
Download Original Figure
Fig. 5.
Histopathologic findings of malignant lymphoma. A : Tumor cells are predominantly large atypical lymphoid cells with abundant cytoplasm and irregular cleaved nuclei (H&E, ×400). B : immunohistochemical stain shows diffuse immunoreactivity for the B cell marker, CD20 (×400). C : Immunohistochemical stain shows cytoplasmic positive lymphoid cells for the B cell marker, Bcl-2 (×400). D : Immunohistochemical stain shows cytoplasmic positive lymphoid cells for the B cell marker, CD79a (×400).
Download Original Figure
원격 전이 여부를 판단하기 위해 시행한 양전자단층촬영(positron emission tomography CT, PET-CT) 및 흉부, 복부 CT에서 우측 경부 level IB 림프절과 좌측 경부 level II 림프절에서 전이 의심 소견 외에 기타 특이 소견은 보이지 않아 Ann Arbor stage IIEA의 병기로 설정되었다.
병기 평가 이후 6회의 R-CHOP(rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, prednisolone) 복합 항암치료를 시행하였으며, 치료 종결 후 완전 관해에 도달하였다. 치료 종결 2년 뒤 마지막 외래 방문 시 특이 호소 증상은 없었으며 재발 소견은 보이지 않았다.
고찰
두경부의 비호지킨 림프종(non-hodgkin’s lymphoma)은 25%–40%에서 림프절 외 침범 양상을 보이며 이는 림프절 외 림프종(extranodal lymphoma)의 대부분을 차지한다.3) 이 중 비강 및 비부비동에 발생하는 비호지킨 림프절 외 림프종은 아시아, 아프리카 인종에서 더 높은 빈도로 발생하는데,4) 대부분 NK/T 세포 림프종이며, 종괴를 형성하기보다는 점막 병변으로 나타난다.5–7) 서양인에서 흔히 발생하는 B세포 림프종의 경우 발생 빈도가 드물며, 비강, 상악동, 사골동에 주로 발생한다.
미만성 거대 B세포 림프종 환자의 증상으로 주로 비폐색, 비루, 안면 종창, 시력저하 등의 종괴 효과가 많으나, 약 1/3에서 고열, 야간 발한, 체중감소와 같은 B 증상도 발생한다.8)
상악동에서 유래한 미만성 거대 B세포 림프종에 대한 방사선 소견은 부비동 내에 국한되는 연조직 종괴로 국소 침윤은 심하지 않는 형태로 관찰된다.9) 비부비동 상피세포악성종양에서 보이는 파괴적이며 침습적인 소견과는 확연히 차이가 나는 불완전한 골파괴 소견을 보이며 골막은 온전하게 남아 있다. 따라서 항암치료 후 재석회화가 나타나 골 조직이 다시 정상으로 돌아오는 특징을 보인다.10) 국내에서는 Koo 등이 접형동에서 발생하여 중두개저를 침범한 미만성 거대 B세포 림프종을 보고11)하는 등 여러 저자들이 발표하였으나 영상 소견상 섬유성 이형성증을 모방한 양상을 보고한 적은 없었다. CT, MRI 등 영상 진단으로 염증성 질환과 종양의 감별진단이 힘든 경우 조직생검으로 조기에 진단하는 것이 중요하다.6)
본 증례에서 두통, 안면통 외에 특별한 전신 증상은 호소하지 않았으며 CT 소견에서 우측 상악동 내의 연조직 음영과 우측 상악골의 간유리 음영을 보이고, MRI 소견에서 T2/T1 강조 영상에서 중간 정도의 신호 강도 및 조영 증강되지 않는 소견을 보여 섬유성 이형성증과 같은 양성 종양에 동반된 상악동염으로 의심하고 절제 생검 및 치료를 위해 수술적 제거를 고려하였다.
확진을 위해서는 조직 검사 시행이 필수적인데 면역 염색을 시행하여 CD19, CD20, CD22, CD79a 중 한 가지 이상의 B세포 표지자에서 양성반응을 보이면, 미만성 거대 B세포 림프종으로 진단된다.9) 추가적으로 Bcl-2 단백질은 25%–50%에서, Bcl-6 단백질은 약 70%에서 발현한다.12) 또한, 복부 및 흉부 CT, PET-CT 등의 영상학적 검사와 필요한 경우 골수 검사, 척수액검사 등을 통해 병기를 결정한다.
비부비동에 발생한 미만성 거대 B세포 림프종의 치료로는 주로 CHOP(cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, prednisone)과 항CD20 단일클론 항체인 rituximab을 병용 투여하는 R-CHOP을 사용한다.13) 복합 항암화학요법만으로도 높은 치료율을 보이지만, 경우에 따라서 국소방사선치료를 같이 시행하기도 한다. 미만성 거대 B세포 림프종의 치료율은 40%–50% 정도로, NK/T 세포 림프종에 비해 결과가 좋다.14) 임상적 병기, 조직학적 분화도 및 환자의 나이가 가장 중요한 예후 인자로 보고하였다.15)
부비동에 발생하는 림프종은 비특이적인 증상과 신체검사 소견으로 진단이 어려우며, 특히 본 증례에서는 상악골의 골 미란이 섬유성 이형성증의 간유리 음영과 비슷한 양상을 보여 부비동염이 동반된 양성 종양으로 판단하여 수술을 시행하였으며, 이후 미만성 거대 B세포 림프종 진단 및 복합 화학요법으로 성공적으로 치료하였기에 문헌 고찰과 함께 보고하는 바이다.