서론
후두기관협착은 선천적 혹은 후천적으로 다양한 원인과 복합적 기전에 의해 발생하며, 주로 상기도 점막의 염증 및 이로 인해 섬유화가 동반되어 상기도 폐쇄를 유발하며 치료가 힘든 질환이다.1,2) 모든 연령에서 후천성 후두기관협착의 가장 흔한 원인은 기관내 삽관에 따른 합병증으로 알려져 있다. 기관내 삽관 시 기관 튜브의 기낭 압력이 기관 점막의 허혈성 손상을 유발하게 되고, 보통은 손상된 점막이 재상피화를 거쳐 회복되나, 점막 손상 및 심한 염증이 지속되면 기관 연골의 이차적 감염으로 이어져 재상피화가 지연되고, 육아 조직이 자라 후두기관협착으로 이어진다. 다양한 원인에 의해서 재상피화의 과정에 이상이 발생할 경우, 반흔 조직이 과형성되면서 후두기관협착이 발생할 수 있다.3)
드물긴 하나, 자가면역질환에서도 생명을 위협하는 후두기관협착이 질환과 연관되어 유발될 수 있다고 알려져 있으며, 육아종증 다발혈관염(granulomatosis with polyangiitis), 재발성 다발성 연골염(relapsing polychondritis), 유육종증(sarcoidosis)이 대표적인 질환들이다.4-6) 자가면역질환과 연관된 후두기관협착은 기존 질환의 염증 반응이 후두에서 악화를 보이는 것으로 생각되며, 현재로서 정립된 표준 치료법은 없는 상태이다.7) 최근 저자들은 자가면역질환과 동반된 후두 기관 협착 2예를 수술적 치료와 전신적 약물 치료로 성공적으로 치료하였기에 문헌 고찰과 함께 보고하는 바이다.
증례
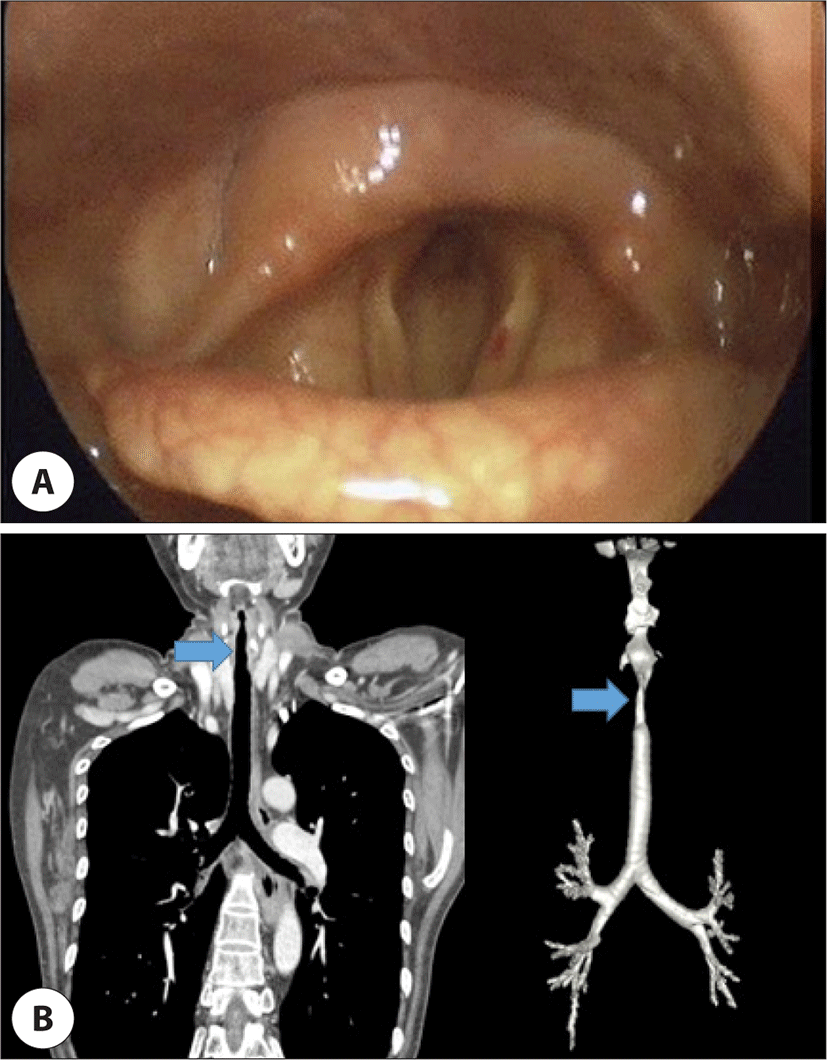
본 환자는 54세 여자 환자로 9개월 전부터 발생한 쉰 목소리 및 호흡곤란 악화로 본원을 방문하였다. 타원에서 좌측 이개 연골염의 과거력 및 성문하 협착 소견으로 재발성 다발성 연골염 진단 하 스테로이드 및 methotrexate, mycophenolate mofetil을 포함한 면역억제제 치료를 시행한 환자였다. 본원에서 시행한 후두내시경 검사에서 양측 성대의 움직임은 이상이 없으나, Myer-Cotton grade II8)의 성문하 협착 소견이 확인되었다(Fig. 1A). 혈액 검사 상 항핵항체(antinuclear antibody, ANA) 역가가 약간 상승된 것 이외 류마티스 질환 관련 자가항체는 음성이었으며, 기도 전산단층촬영(computed tomography, CT) 상에서도 기관 상부의 성문하 협착이 확인되었다(Fig. 1B).
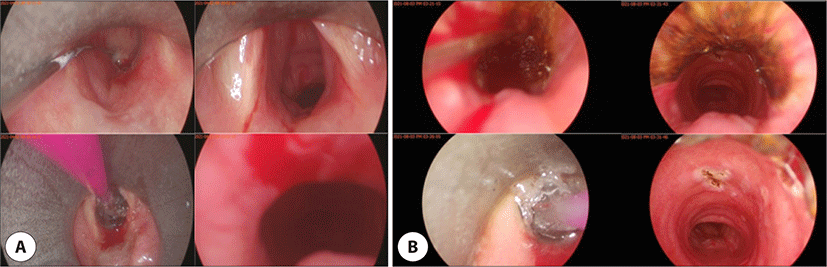
전신마취 하 현수 후두경 검사(suspension exam)를 시행하여 협착 부위에 풍선 확장술 및 triamcinolone 주입술을 시행하였다(Fig. 2A). 수술 후 면역억제제 치료를 재개하며 3개월 가량은 안정적인 상태로 경과 관찰하였으나, 이후 다시 호흡곤란이 발생하여 전신마취 하 재수술을 진행하였다. CO2 레이저를 이용하여 성문하 전방의 섬유성 조직을 제거한 이후, 풍선 확장술 및 triamcinolone 주입술을 시행하였다(Fig. 2B). 이후 환자는 호흡곤란이 호전된 상태로, 류마티스 내과 협진을 통하여 스테로이드 및 methotrexate를 복용하며 수술 후 6개월째 정기적인 경과 관찰 중이며, 재협착의 소견은 보이지 않고 있다.
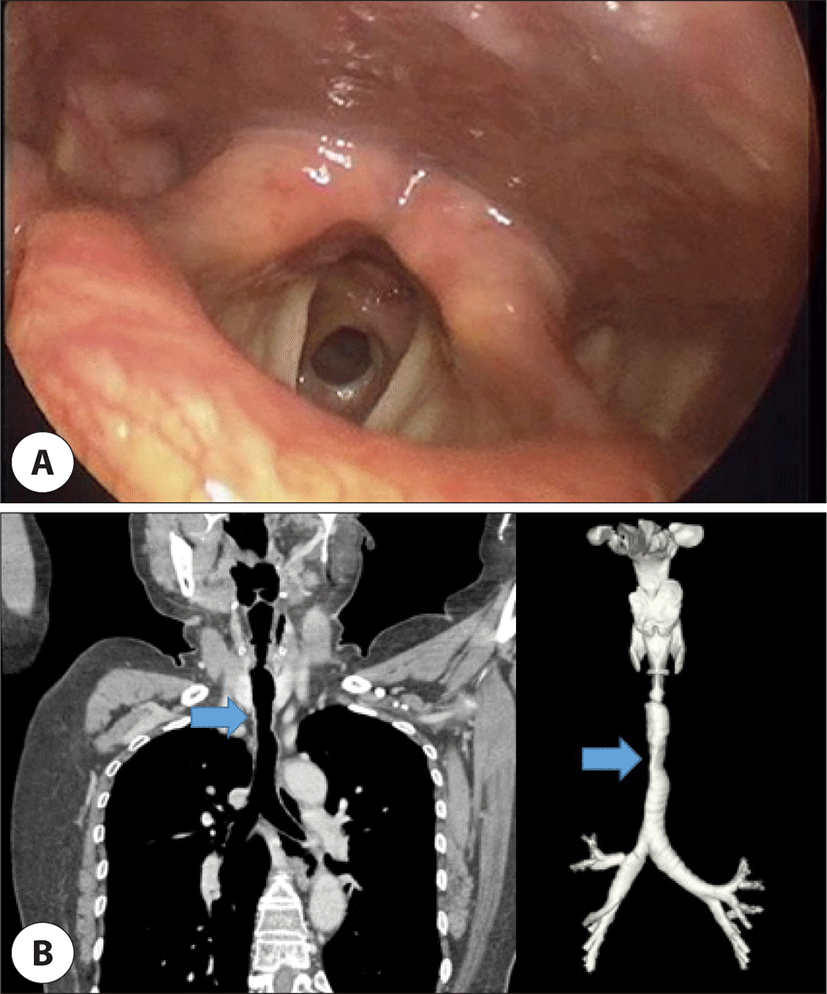
56세 여자 환자가 8개월 전부터 발생한 호흡 곤란 및 목 통증으로 본원을 방문하였다. 6년 전 유방암으로 수술 및 보조 항암화학요법을 시행 받았으며, 16년 전 류마티스 관절염(rheumatoid arthritis)을 진단 받고 스테로이드 및 비스테로이드성 항염증제를 복용해오던 환자였다. 후두내시경에서 양측 성대의 움직임은 이상이 없으나, Myer-Cotton grade II8)의 기관 협착 소견이 확인되었다(Fig. 3A). 혈액 검사 상 류마티스 인자(rheumatic factor)와 항CCP항체(anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody)가 양성이었다. 기도 CT 상에서는 근위부 기관의 협착 소견이 확인되었다(Fig. 3B).
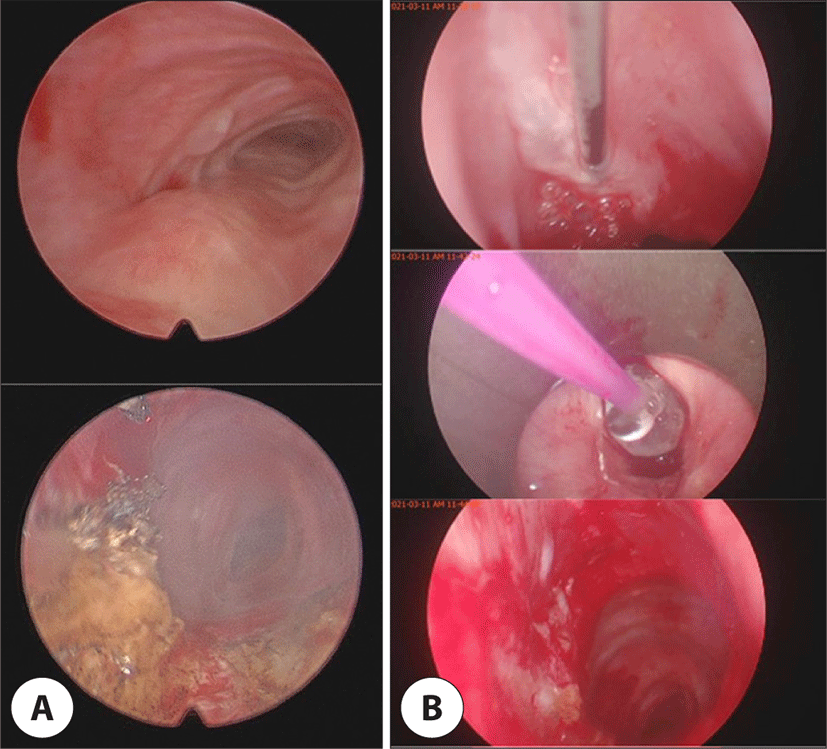
전신마취 하 현수 후두경 검사를 시행하여 기관의 후방 협착 부위를 CO2 레이저로 절제하였고, 풍선 확장술 및 triamcinolone 주입술을 시행하였다(Fig. 4A). 첫 수술 이후 hydroxychloroquine, 스테로이드 및 tacrolimus를 유지하며 경과 관찰하였으나, 주관적 호흡곤란이 지속되었다. 이에 1개월 후 현수 후두경 검사 하 기관 전방의 육아 조직을 절제하고, 풍선 확장술 및 triamcinolone 주입술을 시행하였다(Fig. 4B). 두 차례의 수술 후 호흡곤란은 호전되었고, 류마티스 내과에서 hydroxychloroquine, 스테로이드 및 upadacitinib 투약을 유지하며 외래 통한 경과 관찰 중이며, 수술 후 1년이 지난 현재 재협착은 없는 상태이다.
고찰
연골염에 의해 발생하는 후두기관협착의 경우 적극적으로 수술을 하기 어려운 경우가 많다. 증례 1의 경우는 재발성 다발성 연골염 환자에서 특발성 성문하 협착이 발생하여 두 차례의 수술과 함께 전신적 면역 억제제 치료를 시행하며 안정적인 상태를 유지하고 있는 사례이다. 재발성 다발성 연골염은 매우 드문 자가면역질환으로, 연골 및 proteoglycan이 풍부한 조직에 대한 면역 반응으로 인해 반복적인 염증이 발생하여 침범된 구조물의 해부학적 변형 및 기능적 손상까지 발생할 수 있다. 이개 연골염이 가장 흔하며 비배의 연골부를 침범하면서 안장코가 발생할 수 있고, 관절염, 결막염, 후두 및 기관지 연골까지도 침범 가능하다.9) 재발성 다발성 연골염에서 후두기관협착은 10%-50%의 환자에서 확인되며, 가장 흔한 사망의 원인이 된다. 심각한 기도 폐쇄가 있는 경우에는 응급 기관 절개술 혹은 후두 기관 재건술이 필요할 수도 있다.6)
증례 2의 경우는 류마티스 관절염으로 치료 받던 환자에서 특발성 상부 기관 협착이 발생한 사례로, 두 차례의 수술 및 약물 치료로 호흡 곤란을 치료하였다. 자가면역질환과 별개로 발생한 기관협착으로 우선적으로 진단할 수도 있겠으나, 16년 전 류마티스 관절염을 진단 받고 약물을 복용하며 안정적인 상태를 유지하던 환자가 호흡곤란의 발생과 함께 기존 질환과 연관된 손목, 경부 및 배부 통증이 악화되며, 기존 약물로 조절되지 않음을 호소하였고, 수술과 함께 약물을 변경하여 유지한 면역억제제 치료에 환자의 증상이 잘 조절되었기 때문에 저자들은 임상적으로 자가면역질환과 연관된 증상이라고 판단하였다. 문헌에 따라 다양하긴 하나, 여러 연구에서 류마티스 관절염 환자의 31%에서 75%까지 질환의 후두기관 침범이 있었다고 보고한 바 있다.10) 후두 점막 부종, 후두 내근염, 윤상피열관절(cricoarytenoid joint)의 고정 및 성문하 협착까지 다양한 증상이 발생할 수 있기 때문에 류마티스 관절염 환자에서도 기도 질환이 의심 되는 경우 철저한 후두 내시경 검사를 통한 이른 발견이 중요하다.11)
자가면역질환과 연관된 후두기관협착의 발생 기전과 병인에 대해서 현재까지 충분한 연구 결과 및 명확히 밝혀진 바가 없다. Gelbard 등은 특발성 성문하 협착 환자에서 면역 세포로부터 유래한 interleukin 17A(IL-17A) 및 IL-23의 표현 및 활성도가 유의하게 증가되어 있어 조직 염증과 섬유화를 초래할 수 있음을 분자적 측면에서 처음으로 보고하였다.12) Morrison 등은 연구에서 특발성 성문하 협착 환자의 기관 점막 상처에 상향 조절된 IL-17A가 직접적으로 섬유아세포(fibroblast)의 증식을 초래하고, TGFβ-1과 함께 콜라겐 및 fibronectin과 같은 세포외기질(extracellular matrix)의 생산을 증진시킨다고 밝혔다.13) 류마티스 관절염, 육아종증 다발혈관염과 같은 자가면역 교원 혈관 질환에서 혈액 내 순환하는 IL-17A 양성 세포들이 증가한다는 점에서, 이러한 질환들에서 후두기관협착 발생과의 연관성을 생각해볼 수 있다.12)
자가면역질환에서 후두기관협착이 발생한 경우에는 전신적인 약물 치료와 함께 내시경을 통한 수술적 치료를 함께 시행하도록 하여야 한다. 기관 내 확장술과 함께 스테로이드 주입을 시행하는 것이 환자의 증상을 즉시 호전시킬 수 있는 효과적인 수술적 치료법으로 보고된다.14) 육아종증 다발혈관염과 연관된 성문하 협착 환자에서 leflunomide를 통한 전신 약물 치료를 수술적 치료와 함께 시행 받은 경우 확장술을 시행 받아야 하는 시간 간격을 유의하게 연장시켰다는 보고가 있다.7) 수술적 방법의 차이는 확장술 시행 간격에 유의한 영향을 주지 못하였다는 점을 고려하면, 단순히 수술적으로 협착 부위를 해결하려는 것보다, 자가면역질환의 활성도를 억제할 수 있도록 면역억제제를 포함한 적절한 약물을 적정 농도로 사용하는 개인화된 치료를 시행하는 것이 중요하다고 할 수 있다.14,15) 면역억제치료에 있어 glucocorticoids, cyclophosphamide, azathioprine, dapsone, cyclosporine 등과 같은 약물을 쓰게 되며, 조금 더 공격적인 치료로서 methotrexate 사용까지 고려할 수 있다.6) 따라서 자가면역질환 연관 후두기관협착의 치료에 있어 류마티스 내과 및 이비인후과, 마취과 등 여러 분야의 다학제적 접근 및 향후 여러 면역억제요법의 효능에 대한 연구가 필요하다. 이번 연구에서 소개한 증례의 환자도 지속적인 관리를 통해 기도 확보를 위해 기관단단문합술 또는 부분윤상연골절제술 시행을 고려하였지만, 자가면역질환의 활성도를 예측하기 어려웠기 때문에 증상 개선을 위한 내시경적 수술을 시행하였다. 수술 후에도 면역억제제를 복용하면서 협착 부위가 안정적으로 유지된다면 침습적인 교정 수술보다는 내시경적 수술로 환자의 기도를 확보할 수 있을 것이다.
